Osteochondrosis is the leading cause of back pain. The thoracic spine is affected less frequently than other parts, initially less mobile. Due to the lack of characteristic symptoms, degenerative disease is more difficult to diagnose. Untimely treatment leads to serious consequences.
Degrees and symptoms of osteochondrosis
Dystrophic lesions of bone and cartilage are the most common chronic human diseases. The pathological process begins with the nucleus of the intervertebral disc and then spreads to annular fibrosis. Atrophied cartilage loses its cushioning properties and the load on the bone increases. The gap between the vertebrae is reduced, protrusions and hernias appear, nerve endings are pinched.
Symptoms of pathology:
- dorsalgia (back pain), aggravated by body movements, palpation, deep sighing and coughing;
- discomfort in the sternum on the left side, shortness of breath, feeling of a lump in the throat;
- excessive sweating;
- tingling sensation in part of the skin and limbs;
- painful sensations in the xiphoid process, extending to the shoulders and arms;
- dorsago - acute chest pain when in one position for a long time.
Irritation of the receptors in the spine in the chest area is manifested by impulses that mimic heart disease. This pseudocoronary pain is called anterior chest wall syndrome. The pain in the left side lasts for weeks, is not relieved by heart medications. At the same time, the ECG does not show abnormalities in the work of the body.
The symptoms of the disease are often similar to other pathologies. Patients' complaints may indicate heart failure or gastrointestinal problems. Only a thorough examination will help establish the correct diagnosis.
The clinical picture of the disease varies depending on the compression or non-compression forms of osteochondrosis. When squeezing (compressing) the nerve endings, pain, tingling, muscle weakness and difficulty moving occur. The non-compression form is manifested by a syndrome of acute or chronic pain in the damaged area of the spine, as well as reflex pain in the heart, stomach, liver. The clinical signs of pathology vary depending on the stage of the disease and the age of the person.
Unusual symptoms of osteochondrosis of the breast include women's sensations of breast pain, brittle nails and flaky skin. The disease is triggered by pregnancy. At this time, the female body experiences increased stress on the spine and lack of nutrients.
In men, the compression of the nerve roots in the lower chest area leads to discomfort in the groin area, kidney pain.
Degrees of osteochondrosis
Depending on the condition of the cartilage tissue, 4 degrees of the disease are distinguished:
- Grade 1 - in the early stages of the disease cracks appear in the annular fibrosis. The pulpous nucleus stands out through them. There are unpleasant sensations in the sternum, heart area. This stage is characterized by pulling pains and muscle spasms.
- Grade 2 - the situation is aggravated by the pathological mobility of the vertebrae. A sign at this stage is increased pain when moving and for a long time in one position. Subluxation of the vertebrae is possible.
- Grade 3 - the structure of the spine is severely damaged, the fibrous ring is completely destroyed. Defeat of the nerve endings leads to intercostal neuralgia. A person's mobility is limited, he takes a forced position. The pain radiates to the internal organs, abdomen, limbs.
- Grade 4 - the structures surrounding the spine are involved in the pathological process. Overgrowth of scars leads to fibrosis of the ligaments. A severe neurological reaction requires the regular use of maintenance medications.
Early diagnosis of the disease can delay the destruction of the intervertebral discs. In the early stages, treatment is more effective. In case of prolonged back pain and other symptoms of osteochondrosis, you should consult a neurologist.
The delayed visit to the hospital leads to dangerous complications. These include disc herniation, inflammation of nerve endings, osteophyte proliferation, paresis. As bone growths increase, there is a high risk of damage to spinal canal tissue. The started dystrophic processes are the complete destruction of the vertebrae. The patient can only be helped through surgery.
Causes and risk factors
The mobile cervical and lumbar vertebrae are most often affected by the disease. The chest area is reinforced with ribs, which reduces the risk of pathology, but does not exclude its occurrence. The disease can occur at any age. Its ICD 10 code is M42. 14 - osteochondrosis of the spine in adults with localization in the chest area. There is a separate code for adolescent patients - M42. 0. Poor posture, kyphosis or scoliosis are provoking factors for the onset of the disease in young people.
The main causes of the disease
Degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs occur with malnutrition. The nucleus pulposus loses its ability to distribute the load evenly and cracks appear in the annular fibrosis. Doctors believe that a common cause of pathology is a genetic predisposition to osteochondrosis. Other factors include:
- sedentary lifestyle and sedentary work;
- spinal cord injury;
- infectious diseases;
- increased physical activity;
- hormonal disorders;
- weak muscular corset.
The exact cause of degenerative changes cannot be determined. The disease can be recognized by objective signs and symptoms. People who spend a lot of time in a sitting position, have problems with posture and spinal injuries, should be especially careful about their manifestations.

Provoking factors
The natural tendency to cartilage dystrophy can only appear in middle age, when the body's natural aging process begins. But there are factors that can provoke accelerated degeneration. They include:
- chronic stress;
- hypothermia;
- unbalanced diet;
- difficult working conditions;
- Overweight.
Prolonged pinching and inflammation of the nerve roots cause disorders of the internal organs. Osteochondrosis is characterized by a wavy course, periods of acute or dull pain are replaced by remission.
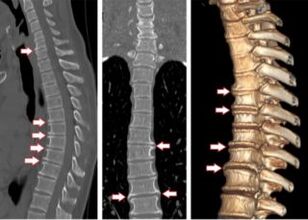
Diagnostic methods
To make a diagnosis, you will need to collect the patient's history, perform a physical examination. A preliminary conclusion is made during the initial examination. The patient's spine is examined in different positions. Confirmation of the pathology and information about the condition of the spine is provided by instrumental diagnostics. The experts use:
- Radiography. Photographs of the thoracic region show the degree of pathology. Direct and lateral radiographs help to detect changes in disc height, the appearance of osteophytes, the thickening of the end plates of the spinal body, the narrowing of the diameter of the spinal canal, and the formation of Schmorl's nodules.
- Computed tomography is performed to detect and measure bone structures.
If necessary, magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed.
Treatment and prevention
Getting rid of pain, inflammation and other problems is possible only with complex treatment. The choice of technique depends on the patient's condition. In the initial stages, conservative therapy is practiced; in advanced cases, surgery will be required.
Medicines
A course of treatment is prescribed to eliminate the pain and prevent further destruction of the structures of the intervertebral disc. The basis of therapy is nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They are prescribed in the form of tablets and ointments.
Hormonal drugs - corticosteroids - are used to treat 3 degrees of osteochondrosis. They have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. In acute pain syndrome, anesthetic injections are indicated. Muscle spasms and tension are relieved by muscle relaxants. To restore cartilage tissue, experts advise to use chondroprotectors.
The cure of inflammation of the nerve roots is facilitated by the intake of special vitamin complexes containing B vitamins. Useful elements are well absorbed from food - eggs, herbs, beef and cheese. The patient is advised to rest and rest. He should observe bed rest during the first days.
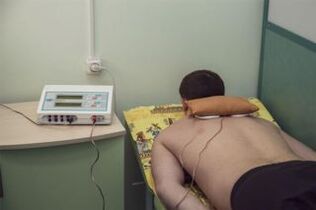
Physiotherapy
The effect of the device has a pronounced therapeutic effect. Patients with osteochondrosis are prescribed:
- shock wave therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- ultrasonic exposure;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy.
Physiotherapy improves blood flow and relaxes muscles. During electrophoresis sessions, the drugs penetrate deeper into the tissues of the body.
Folk remedies
You can treat yourself not only with drugs, but also with the help of folk remedies. At home, various herbs and foods can be used as medicine. Decoctions, ointments, rubbing are prepared from them. The means allow to alleviate the inflammation, to accelerate the regeneration processes. A warm bath with sea salt and chamomile helps relieve pain. Effective recipes:
- Juniper and oil ointment - beat the crushed juniper with oil until smooth. The composition is stored in a refrigerator.
- Pork hotplate ointment and hop cones - the dry cones are ground to a powder and mixed with fat. The ointment is applied 2-3 times a day.
- Honey compress - for the composition you need 2 tablespoons of honey, 2 tablespoons of vodka, 1 tablespoon of aloe juice. The products are mixed and applied to the affected area.
- Mustard compress - vodka, camphor alcohol and mustard powder are mixed in equal proportions. Add 3 proteins and incubate for 12 hours. The product has an irritating effect, so use with caution.
Before using the compositions, doctors advise to check them for an allergic reaction.
Massage
One of the parts of the complex treatment of osteochondrosis of the chest is massage. The procedure reduces pain, increases blood circulation and stimulates muscles. Applicators can replace massage and acupuncture at home. These are special carpets with plastic needles.
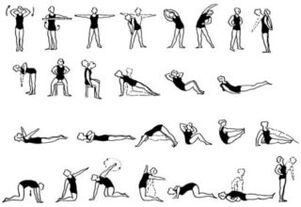
Physiotherapy
When the period of exacerbation is over, it is recommended to switch to light physical activity. These include walking, swimming, yoga and therapeutic gymnastics. Performing a special set of exercises is the easiest way to deal with illness and forget about back problems forever. During the exercises the emphasis is on stretching and strengthening the chest muscles. There is a special technique that helps to improve the health of the spine. The exercises are selected according to the individual characteristics of the patient.
Preventive recommendations
Doctors advise as a prevention of the disease to regularly perform a set of exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles of the back and chest. In addition to gymnastics, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Take breaks while doing sedentary work. Change your posture often so that the load is distributed between different muscle groups.
- Choose a comfortable orthopedic mattress for a good rest of the spine.
- Use chairs with a high back that supports the spine.
- Balance your diet.
- Refuse to lift and carry weights.
A timely visit to the doctor allows you to diagnose osteochondrosis at an early stage. This gives a favorable prognosis for recovery.



































